- The brain with metastasis
Microglia, macrophages
- Why are microglia/macrophages linked to all brain disorders, including brain metastasis?
STAT3 labels a subpopulation of reactive astrocytes required for brain metastasis.
Priego N et al. Nature Medicine. (2018).
The potential of astrocytes as immune modulators in brain tumors
Priego N and Valiente M. Frontiers in Immunology. (2019).
Protocol to generate murine organotypic brain cultures for drug screening and evaluation of anti-metastatic efficacy
Lucía Zhu, Lauritz Miarka, Patricia Baena, María Perea-García, Manuel Valiente. STAR Protocols (2023)
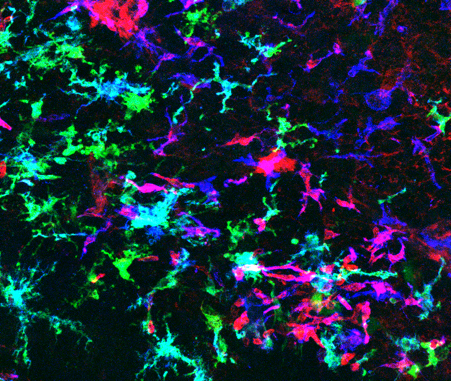
Being both resident cells (microglia) and cells infiltrating from peripheral circulation (bone marrow-derived macrophages, BMDM) they create an ecosystem that only appear in the presence of a brain damage, such as brain metastasis. BMDM will never get into the brain unless it is altered. Once there together with the microglia they are supposed to help keeping the function of the brain intact defending it from the invasive tumor, however what happens it is quite the opposite as time progresses. Microglia/ macrophages becomes important contributors to brain metastasis local progression.
We are trying to identify the biology of macrophage/ microglia rewiring in the contect of brain metastasis. A lot has been done already in the field but we are particularly interested in how the cell behavior is influence by a wider cellular network of cancer and non-cancer cells.
We have established a connection between microglia/macrophages and astrocytes by which the reactive glial cell activates a pathway in microglia/macrophages with a remarkable influence on putting them to work for the metastasis.
We are digging as deep as possible in this signalling pathway within microglia/macrophages not only to understand the underlying biology but to explore whether we can target it, thus, aiming to impair the microenvironment corsstalk we think is critical to impair the formation of a pro-metastatic environment in the brain.
Why are microglia/macrophages linked to all brain disorders, including brain metastasis?
We are deconstructing this signalling pathway within microglia/macrophages not only to understand the underlying biology but to explore whether we can target it. We hypothesize that impairing the microenvironment crosstalk is critical to impair the formation of a pro-metastatic environment in the brain.